

Alopecia universalis – complete loss of body hair.Affects up to 5% of patients with autoimmune hair loss.Alopecia totalis – complete loss of scalp hair.The scalp is most commonly affected, but may also affect the: Well- demarcated single or several round/oval patches of normal-appearing skin.Patchy alopecia areata is the most common pattern, producing: What are the clinical features of alopecia areata?Īcute onset of hair loss may manifest in a number of patterns. Mode of inheritance appears to be complex, with environmental influences also at play.Include numerous human leukocyte antigen ( HLA) class I and II alleles, and several alleles of genes involved in immune pathways, hair pigmentation, and response to oxidative stress.At least 16 genetic risk loci have been detected.Alopecia areata has a strong hereditary component.This hypothesis is supported by the observation of a dense perifollicular infiltrate of T cells on histopathological examination of anagen follicles in alopecia areata an area that is normally sparse of immune cells. Subsequent autoimmune attack of the anagen follicle causes premature transition of the follicle into the telogen phase with ultimate loss of the hair.Protective immune privilege may be lost in alopecia areata, allowing hair follicle autoantigens to be presented to autoreactive CD8+ T cells.Normal anagen hair follicles are thought to exhibit immune privilege, rendering them exempt from immune surveillance and protected against autoimmune attack.It is hypothesised that loss of immune privilege in anagen hair follicles plays a key role in the pathogenesis, and genetic susceptibility is also thought to contribute. The exact mechanism responsible for hair loss in alopecia areata remains unclear. Telogen is the resting phase lasting several months.Catagen is a short involution phase lasting several weeks.Anagen is the active growth phase lasting one to eight years.Certain susceptibility genes (see below).Ī normal hair follicle cycles through multiple phases:.Other autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo and thyroid disease.Polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type 1.Chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome.
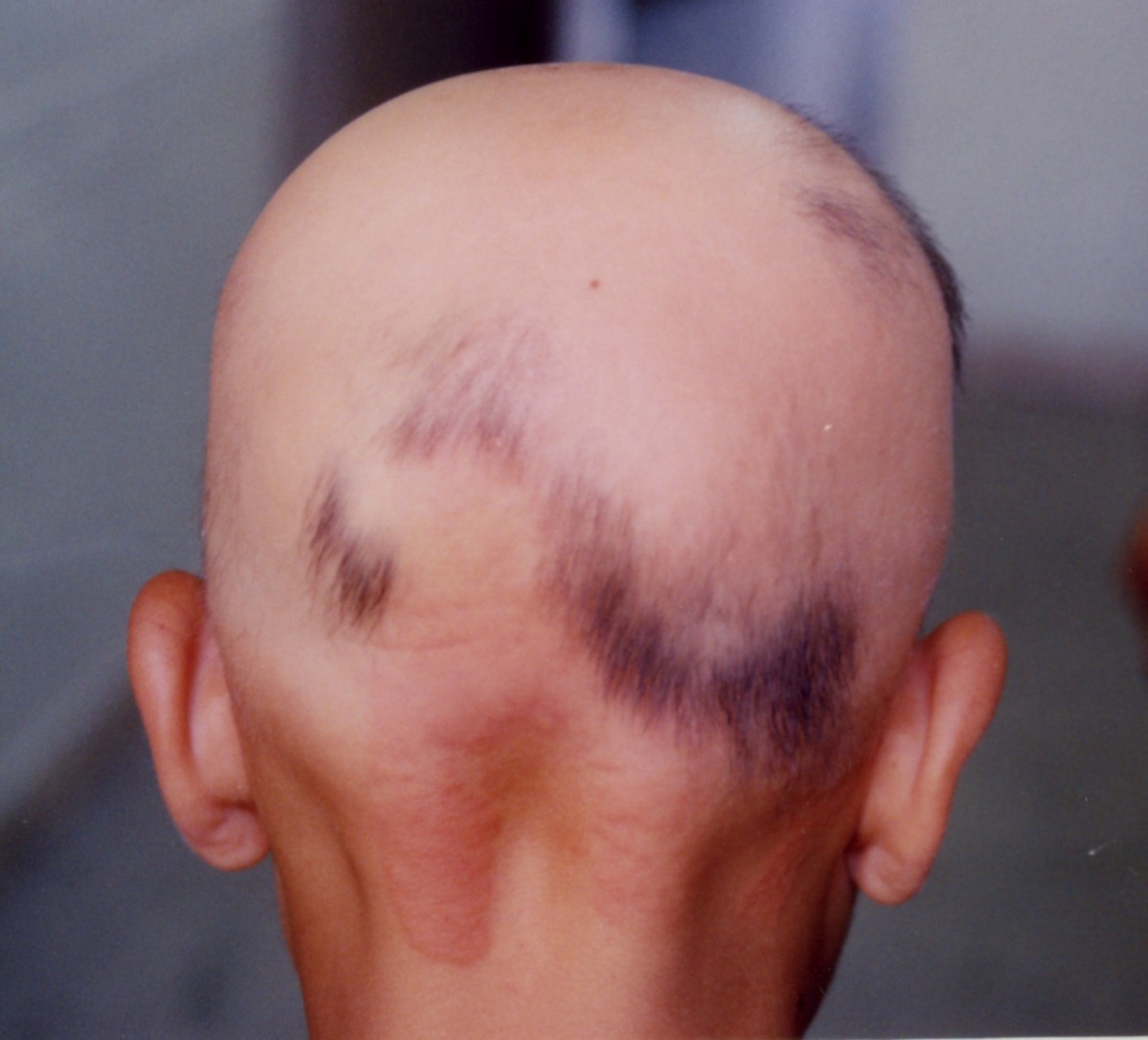
The following may increase the risk of alopecia areata: Alopecia areata does not carry significant sex or ethnic predominance. Peak incidence occurs in the second and third decades and most patients experience onset before the fourth decade.
ALOPECIA AREATA UNIVERSALIS TREATMENT SKIN
It affects children and adults of all skin and hair colours. The lifetime risk of alopecia areata is approximately 2%. Click here for more images Who gets alopecia areata?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
